You’ve just finished crafting an incredible piece of content—the kind you’re sure Google wants to rank. It’s packed with valuable tips, smart strategies, eye-catching visuals, screenshots, and even multimedia. Lots of people in your industry will definitely want to link to it—or so you think.
You hit publish…
And then—crickets.
Maybe it’s stuck on page two of Google. For months. Maybe it’s getting traffic, but no one’s converting.
So, what went wrong?
The question is: did you optimize it for SEO keyword intent?

What Is User Intent in SEO
When someone types a question into Google, they’re on a mission. Maybe they’re looking for an answer, shopping for something, or just trying to find a specific page. That’s SEO keyword intent or simply search intent—the real reason behind their query. Some even call it Central Search Intent (CSI).
And guess what? Google and other search engines are obsessed with SEO keyword intent. Their entire goal is to serve up results that perfectly match what users are looking for. Google even released a report called “How Search Intent Is Redefining the Marketing Funnel.”
So, if you want to rank, your content needs to mirror that SEO keyword intent as closely as possible. The more your page fully satisfies SEO user intent, the better it’ll perform.
Of course, great SEO isn’t just about intent—things like backlinks also play a role. But nail the search intent first, and you’re already ahead of the game.
Why Is Search Intent Important?
When you really understand search intent for SEO, your entire SEO strategy becomes more focused—and more effective. Instead of just chasing traffic, you attract the right visitors who are actually interested in what you offer.
Optimizing for search intent categories means:
1. Higher Rankings
Google (and other search engines) are obsessed with giving users the best answers to their questions.
If your content aligns with SEO keyword intent, Google will rank it higher, leading to more visibility and traffic.
2. Better Conversion Rates
Getting more visitors is great, but what really matters is turning those visitors into customers. By targeting transactional intent keywords, you ensure your product pages and CTAs guide ready-to-buy users toward making a purchase.
Also when your SEO strategy is focused on search intent optimisation naturally you will shape your marketing funnel strategy.
Now you know the intent behind a set of keywords meaning you can write content that guide users through different funnel stages:
- TOFU (Top of Funnel) – Informational search intent: Here your customers are still researching. Your content can educate them and nudge them toward the next step in the buyer’s journey. Content includes blog posts, guides, explainer videos.
- MOFU (Middle of Funnel) – Commercial intent keywords: Commercial intent keywords play a role in helping potential buyers make decisions. Content types include comparisons, case studies, reviews.
- BOFU (Bottom of Funnel) – Transactional intent keywords: Target these keywords in product pages, pricing details, CTAs type of content that naturally leads to more sign-ups, purchases, and conversions.
3. Better User Experience
People stick around when they find what they need—fast. Search intent helps you structure your content in a way that makes sense for different users:
- If someone wants an in-depth guide(informational intent keywords), a long-form article with detailed insights will keep them engaged.
- If they need quick answers, a bullet-pointed FAQ or a well-organized table might be the best format.
When users find value in your content, they stay longer, engage more, and are less likely to bounce—signals that tell search engines your site is worth ranking.
4. Targeting the Right Keywords
Starting with keyword intent in SEO helps you focus on keywords that actually matter—keywords that have strong search volume and bring in the right kind of traffic.
Instead of chasing every keyword out there, you’ll be able to prioritize the ones that lead to real results, making your Intent-based SEO strategy more efficient and cost-effective.
5. Building Authority and Trust
When your content consistently provides the right answers, people start to trust your brand. Understanding search intent meaning, helps you create content that reinforces your expertise.
They’ll come back for more information and, eventually, your products or services. This also boosts your credibility in Google’s eyes, leading to even better rankings over time.
6. Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR)
SEO keyword intent doesn’t just help with rankings—it also improves how many people actually click on your content.
By optimizing your titles and descriptions to match what users are looking for(Google user intent), you make your search results more appealing. When users see that your page has exactly what they need, they’re much more likely to click.
7. Stay Ahead of Trends with Search Intent
Regularly monitoring intent in SEO ensures your content remains relevant, timely, engaging, and aligned with what your audience is actively searching for.
As technology, seasons change so do user behavior and SEO keyword intent Google evolve. Keeping up with trends gives you a competitive edge.
What are The Different Types of Search Intent
To nail SEO keyword intent, you need to understand its core types:
1. Informational Intent – “I Need to Learn”
People with informational search intent are looking for knowledge, how-tos, or explanations.
🔎 Example searches:
- “How to fix a leaky faucet”
- “What is content marketing?”
- “Best time to plant tomatoes”
These users aren’t necessarily ready to buy yet, but by providing useful, clear content, you can build trust—and maybe even guide them toward a purchase later.
2. Navigational Intent – “Take Me There”
This type of search is all about finding a specific website or page. The user already knows where they want to go, they just need a shortcut.
🔎 Example searches:
- “LinkedIn login”
- “Nike official site”
- “Apple customer support”
While you can technically rank for these terms, don’t expect massive traffic. If someone searches “Facebook login,” they’re almost certainly clicking on Facebook—not a third-party website.
3. Transactional Intent – “I’m Ready to Buy”
Users with transactional intent keywords know what they want and are ready to take action. They’re looking for a product, service, or sign-up page—not an article.
🔎 Example searches:
- “Buy wireless headphones online”
- “Discounted MacBook Pro”
- “Sign up for Netflix”
If you’re optimizing for transactional intent, focus on product pages, strong CTAs, and a seamless buying experience—not long-form content.
4. Commercial Investigation – “Which One Is Best?”
Commercial intent keywords signal users who are planning to buy soon but need help deciding between options.
🔎 Example searches:
- “Best tools for intent search engine analysis”
- “Ahrefs vs SEMrush for search intent categories”
- “Top-rated SEO software for keyword intent in SEO”
This is where comparison guides, product reviews, and detailed breakdowns shine. If you provide valuable insights, you can influence their final decision.
5. Ambiguous Intent – “I’m Not Sure”
Search intent isn’t always black and white. Some searches can fall into multiple categories. For example, “SEO audit” could mean:
- A guide on search intent optimization (informational intent)
- A tool recommendation (commercial intent)
- A service page (transactional intent)
The key? Pick one intent and optimize for it fully. Google rewards clarity, so create content that best serves one specific searcher’s needs.
Make your content a perfect match for search intent—one-to-one. Do it right, and you might even land a Featured Snippet. It’s simple: align your content with keyword intent in SEO. Then, add backlinks and other solid SEO strategies, and let Google do the rest.
How to Optimize for Search Intent in SEO
If you want your content to rank well and attract the right audience, you need to match what people are actually searching for.
Optimizing your site for search intent in SEO begins with your keyword intent.
Step 1: Understand Keyword Intent
Not all keywords are created equal.
People search with different goals in mind, and the search terms they use for search usually fall under the different search intent categories:
- Informational – The user wants to learn something. (Example: “How does intermittent fasting work?”)
- Navigational – They’re looking for a specific website or brand. (Example: “Nike running shoes site”)
- Commercial – They’re considering options before making a purchase. (Example: “Best budget smartphones under $500”)
- Transactional – They’re ready to buy or take action. (Example: “Buy Samsung Galaxy S23 online”)
You can often tell a keyword intent in SEO just by looking at it, but don’t stop there—always check the actual search results to confirm. There are two ways to do this:
Analyze the Top-Ranking Pages(Google search intent results)
Google’s top results reveal a lot about SEO keyword intent and what users expect to see. If you want to rank, your content needs to align with what’s already working. Check for:
- Title tags & meta descriptions: Are the top results blog posts, product pages, or comparison articles?
- Content format: Do searchers prefer step-by-step guides, videos, or list-based articles?
- Engagement signals: Are the top-ranking pages interactive, featuring FAQs, embedded media, or user comments?
For example, let’s say you’re researching the keyword “best home espresso machines”.
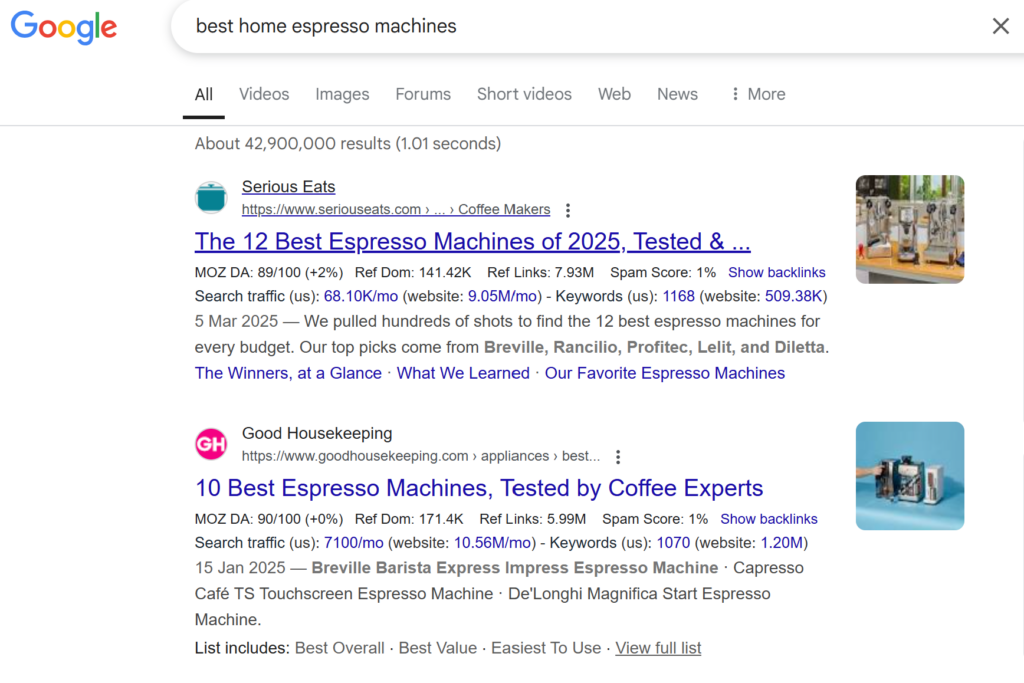
As you can see, the first two results are review articles comparing different models. That signals informational or commercial intent rather than transactional. That tells you searchers want recommendations—not just a single product page.
But if you search “buy Breville Barista Express”, you see retail product pages.
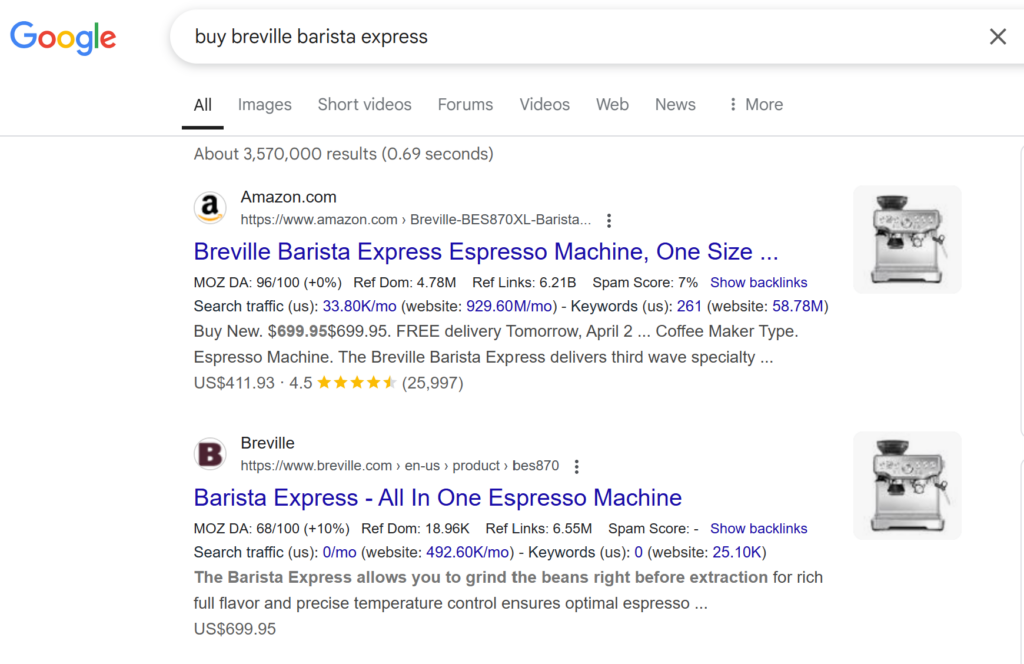
That’s a strong sign users are ready to make a purchase. In this case, Google user intent suggests users are ready to make a purchase, so product pages dominate.
Conduct Keyword Research with Intent in Mind
Basic keyword research won’t cut it—you need user intent optimization to find the perfect opportunities. Here’s how:
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to discover long-tail keywords matching different search intent categories.
- Segment your keywords based on intent:
- For informational intent, create blog posts, how-to guides, or FAQs.
- For commercial intent, publish product comparisons or buyer’s guides.
- For transactional intent, optimize product and landing pages.
A keyword tool like semrush can easily tell you a keyword’s intent.
Step 2: Optimize Your Content for Search Intent
Now that you’ve figured out the right keywords, it’s time to create content that truly matches what users expect when they search. This means optimizing for on-page SEO—but with SEO keyword intent in mind.
Your goal? Make sure your content delivers exactly what searchers are looking for.
1. Match The Type of Content with User Intent
Search intent in SEO isn’t just about the keywords—it’s about the type of content searchers expect to find. If you don’t align with that, Google won’t rank you well (and users will bounce fast).
1. Analyze the Top-Ranking Pages
Before you start writing, check what’s already ranking for your target keyword. This helps you understand what Google considers the best fit for that query and ensures your content aligns with search intent optimisation.
Here’s what to look for:
Content Type: Are the top results blog posts, product pages, videos, or comparison articles?
Format: Are they step-by-step guides, listicles, reviews, or in-depth resources?
Featured Snippets & SERP Features: Are there FAQs, “People Also Ask” boxes, or knowledge panels?
For example, if you search “how to take care of indoor plants”, you’ll mostly find long-form guides with step-by-step instructions. That tells you that if you want to rank, you should create a detailed, beginner-friendly guide—not a short, generic post.
But if you search “buy indoor plant fertilizer,” you’ll see e-commerce product pages. That means searchers are ready to buy, so your content should focus on product listings, pricing, and CTAs rather than educational content. Understanding Google SERP intent helps you make this distinction.
2. Create the Right Type of Content for Each SEO keyword Intent
Once you know what works, tailor your content accordingly:
📝 Informational Search Intent (People looking for knowledge)
- Best Content Types: Blog posts, how-to guides, tutorials, FAQs
- Example Query: “How to fix a leaky faucet”
- What to Create: A step-by-step guide with images or a short video tutorial
- Informational intent keywords: “how to,” “guide,” “tips,” “best ways to”
Transactional Intent Keywords (People ready to buy)
- Best Content Types: Product pages, landing pages, checkout pages
- Example Query: “Buy noise-canceling headphones”
- What to Create: A product page with features, reviews, and a strong “Add to Cart” button
- Transactional intent keywords: “buy,” “purchase,” “discount,” “free shipping”
Commercial Intent Keywords (People researching before buying)
- Best Content Types: Comparison posts, buyer’s guides, roundups
- Example Query: “Best running shoes for beginners”
- What to Create: A detailed comparison post with pros, cons, and price breakdowns
- SEO keyword intent: “best,” “top,” “review,” “vs.”
Navigational Search Intent Examples (People looking for a specific brand or site)
- Best Content Types: Homepage, about pages, brand-specific landing pages
- Example Query: “Nike Air Max official site”
- What to Create: A brand-focused page with easy navigation to product categories
- Keyword intent in SEO: “official site,” “login,” “contact”
Step 3: Optimize for User Experience (UX)
You’ve created the perfect piece of content—one that matches exactly what users are searching for.
But here’s the catch: if your site delivers a bad experience, your visitors may never stick past the first headline.
Google knows this, too. Its algorithms pay close attention to how people interact with search results. If users click on your page but bounce back to Google within seconds, that’s a red flag. It signals to Google that your content isn’t satisfying their intent, and your rankings could take a hit.
So make sure visitors find what they need—easily and quickly—so they stay on your page. Here’s how:
1. Make Your Content Easy to Read
People don’t read web pages—they scan them. So, structure your content in a way that makes skimming effortless. Break down your answers into bite-sized, digestible pieces.
✅ Use short paragraphs (2-3 sentences max)
✅ Break things up with bullet points
✅ Bold key takeaways to make them stand out
✅ Use clear headings (H2s & H3s) that guide users through your content
💡 Example: Instead of one long block of text, organize your how-to guide into numbered steps, with images or subheadings for clarity.
2. Keep Popups to a Minimum
Popups are annoying—Google knows it, and so do your users. If you must use them, stick to exit-intent popups (ones that only appear when a user is about to leave). That way, they don’t disrupt the reading experience.
3. Use Readable Fonts (At Least 14px)
Even the best-written content won’t matter if users struggle to read it. A font size of at least 14px (ideally 16px) ensures clarity. Also, choose fonts that are clean and easy on the eyes.
4. Add Visuals (Images & Videos)
Walls of text are intimidating. Break things up with images, infographics, and videos to keep readers engaged.
- Explaining a complex topic? Add a simple diagram.
- Writing a step-by-step guide? Use screenshots or GIFs.
- Reviewing a product? Include a short video demo
5. Optimize for Mobile
More than half of searches happen on mobile devices. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’re losing visitors fast. Use a responsive design and test your pages on different screen sizes.
6. Speed Matters
No one sticks around for a slow-loading site. Check your speed with Google PageSpeed Insights or GTMetrix—then make improvements like optimizing images and reducing unnecessary scripts.
7. Easy Navigation = Happy Users
If users can’t find what they need in seconds, they’ll bounce. To make your navigation seamless use clear menus, keep text easy to read and make calls to action (CTAs) stand out.
Step 4: Craft Click-Worthy Titles & Meta Descriptions
Your title tags and meta descriptions are like the front door to your content—make them inviting.
A great title should do two things:
✅ Clearly reflect what the content is about in a way that mirror its search intent in SEO.
✅ Be compelling enough to make users want to click.
Think of it this way—your audience is scrolling through search results. What makes them choose your link over the others? A boring, vague title won’t cut it.
A clear, relevant and engaging one will.
Example:
“Best Laptops 2024” → Too generic.
“Best Laptops for Students in 2024 (Affordable & High-Performance)” → Matches user intent in SEO and adds value.
Step 5: Get Noticed with Structured Data & Snippets
🔹 Use Schema Markup
Adding structured data helps search engines understand your content better, increasing your chances of appearing in rich results.
🔹 Optimize for Featured Snippets
Want to land in Google’s “position zero” (the top answer box)?
👉 Structure your content using lists, tables, or direct answers to common questions.
Example: If your post is about “How to Fix a Leaky Faucet,” include a step-by-step list. Google loves pulling clear, scannable answers into featured snippets.
Step 6: Improve Your Existing Content for SEO Keyword Intent
Search intent optimisation isn’t just for new content—your old content can still work wonders with a few strategic updates.
If you’ve got blog posts or pages that are still valuable but not performing as well as they could, don’t scrap them—refresh them.
In fact, re-optimizing old content is one of the fastest ways to boost your organic traffic.
A full content audit can help you identify opportunities, but even small tweaks can make a big impact.
Understanding SEO keyword intent is key to ensuring your existing content still meets users’ needs and ranks higher in search results.
How to Improve Your Existing Content For Search Intent In SEO
The “People Also Ask” section in Google search results is a goldmine of SEO keyword intent insights.
It tells you exactly what questions people have about your existing topic. It shows what users really want to know beyond their initial query. If you answer these questions in your existing content, you improve their relevance and engagement.
💡 Example: If your blog post is about “How to Start a Blog” and you see related questions like:
- “How much does it cost to start a blog?”
- “What is the best platform for beginners?”
- “How do bloggers make money?”
👉 Update your post to include those answers. This not only improves your content for search intent for SEO but also increases its chances of ranking in featured snippets.
Google rewards content that fully satisfies SEO user intent. By revisiting and improving your existing pages, you make them more relevant, more helpful, and more likely to rank higher in search results.
So before rushing to create new content, see what you can improve first. A few tweaks might be all it takes to turn an old post into a traffic magnet.
Optimizing for SEO Keyword Intent Is Not a One-and-Done Thing: Analyze User Behavior and Adjust Accordingly
Getting your content right is just the beginning. Search intent in SEO can change, and so should your content strategy. Keep an eye on how users interact with your pages and adjust accordingly.
✅ Check Your Analytics – Use Google Analytics and Search Console to spot pages with high bounce rates or low engagement. If people aren’t sticking around, your content may not fully match their intent.
✅ Improve Content Quality – If something feels off, tweak it. Add more depth, break up text for easier reading, or include visuals and multimedia to keep users engaged.
✅ Experiment with Different Formats – Not every audience prefers the same thing. If text-heavy content isn’t working, try a video, infographic, or interactive elements to improve engagement.
Google watches user behavior—click-through rates, bounce rates, and dwell time. If people leave your page too fast, Google may decide your content isn’t a great fit for that query. Intent-based SEO means continuously refining your content to align with what users actually want.
Do you have issues figuring keyword intent in SEO? If you are stuck feel free to text me. I enjoy researching keywords and writing content to optimize for search intent. My technique begins with your brand, and ensures who you are gets the right visibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the concept of “search intent” relate to Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO and Search Intent work together to improve search rankings and user experience, but they focus on different aspects of search optimization.
1. Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO focuses on optimizing content to improve its relevance based on meaning, context, and relationships between words.
It goes beyond basic keywords and focuses on meaning, relationships between topics, and how search engines interpret content.
It aims to help search engines understand concepts rather than just keywords.
Key Elements include:
- Topic Clusters & Context – Covers related subtopics, not just a single keyword.
- Entity-Based Optimization – Uses structured data and knowledge graphs.
- Synonyms & Variants – Optimizes for different ways users express the same idea.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – Aligns with how Google understands language.
Example:
Instead of targeting just “best running shoes,” Semantic SEO ensures your content includes related terms like “cushioning,” “trail running,” “arch support,” and “pronation.”
2. Search Intent/SEO Keyword Intent
Search intent is the main force behind a user’s query—why they are searching for something. Google categorizes intent into four main types:
- Informational – Looking for knowledge (e.g., “how to choose running shoes”).
- Navigational – Searching for a specific site or brand (e.g., “Nike official website”).
- Transactional – Ready to buy or take action (e.g., “buy Nike running shoes online”).
- Commercial Investigation – Comparing options before purchasing (e.g., “best running shoes for flat feet 2024”).
Key Elements:
- Keyword Modifiers – Words like “best,” “vs,” “cheap,” or “how to” indicate intent.
- Content Alignment – Your page type (blog, product page, comparison guide) should match what users expect.
- SERP Analysis – Checking Google’s top-ranking pages for a query to understand intent.
While Semantic SEO helps Google understand broader meanings and related topics, Search Intent ensures your content meets the needs of the user at that moment.
To ensure best results, aim at using both—creating in-depth, context-rich content that also aligns with the user’s intent.
Need help optimizing a specific page for Semantic SEO or SEO keyword intent? Leave a message